The original title of the following article is Cause-related Marketing: Another Way of Corporate Charitable Donation in China.
Authors
Giana Lin, giana.lin@fuguanlaw.com, Partner, The FUGUAN Law Firm (B Corp Certified)
Yifei Li, yifei.li@fuguanlaw.com, Lawyer, The FUGUAN Law Firm (B Corp Certified)
Introduction
Charitable donation is one of the most common ways for enterprises, both in China and abroad, to participate in charitable causes and fulfill their social responsibilities. In China’s charity legal system and corporate donation practice, enterprises can make donations through cause-related marketing in addition to directly providing donations to charitable organizations.
What Is Cause-related Marketing?
Cause-related marketing (also known as “cause marketing” and “public welfare-related marketing”) generally refers to the marketing behavior of enterprises with specific meanings, in which the enterprises claim that they will donate a certain amount of revenue from marketing to charitable causes in order to stimulate public consumption, which has combined the realization of business objectives and the support for charitable causes.
From the perspective of charitable organizations, cause-related marketing can help them obtain more funds, contribute to the public’s awareness of their establishment and purposes, and expand their reputation. From a business perspective, cause-related marketing is undoubtedly a marketing method enterprises adopt to create profits. In many countries, it is included in the category of charity law because it includes charitable donation, charitable organization brand, public charity psychology, and other charitable factors, as in the cases of “commercial participator” under the Charities Act 1992 in the United Kingdom, and “Commercial Co-venture (CCV)” in some states in the United States.
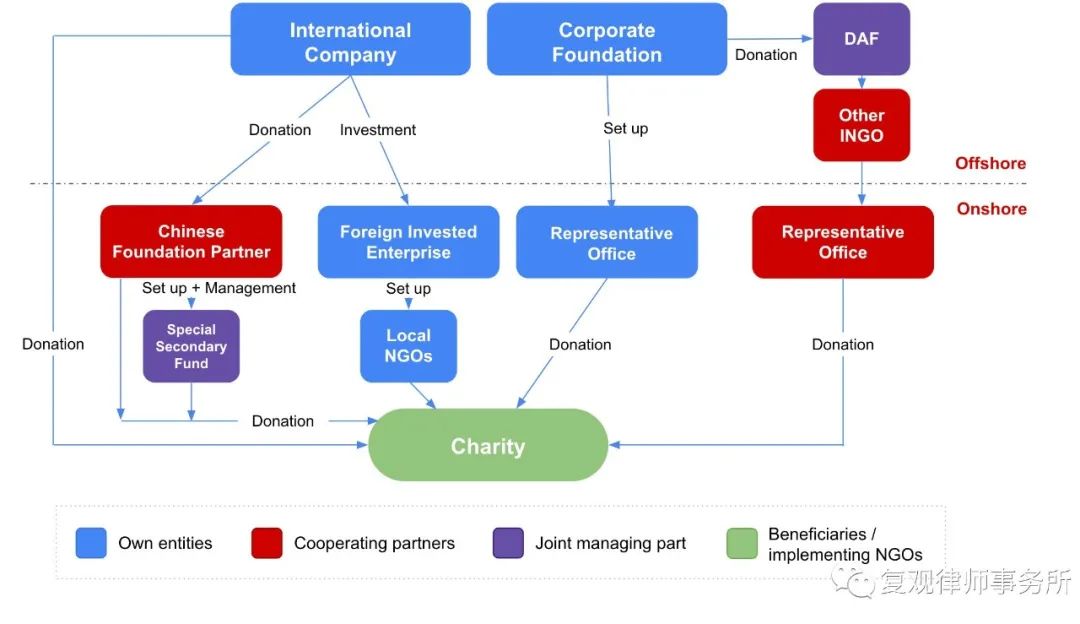
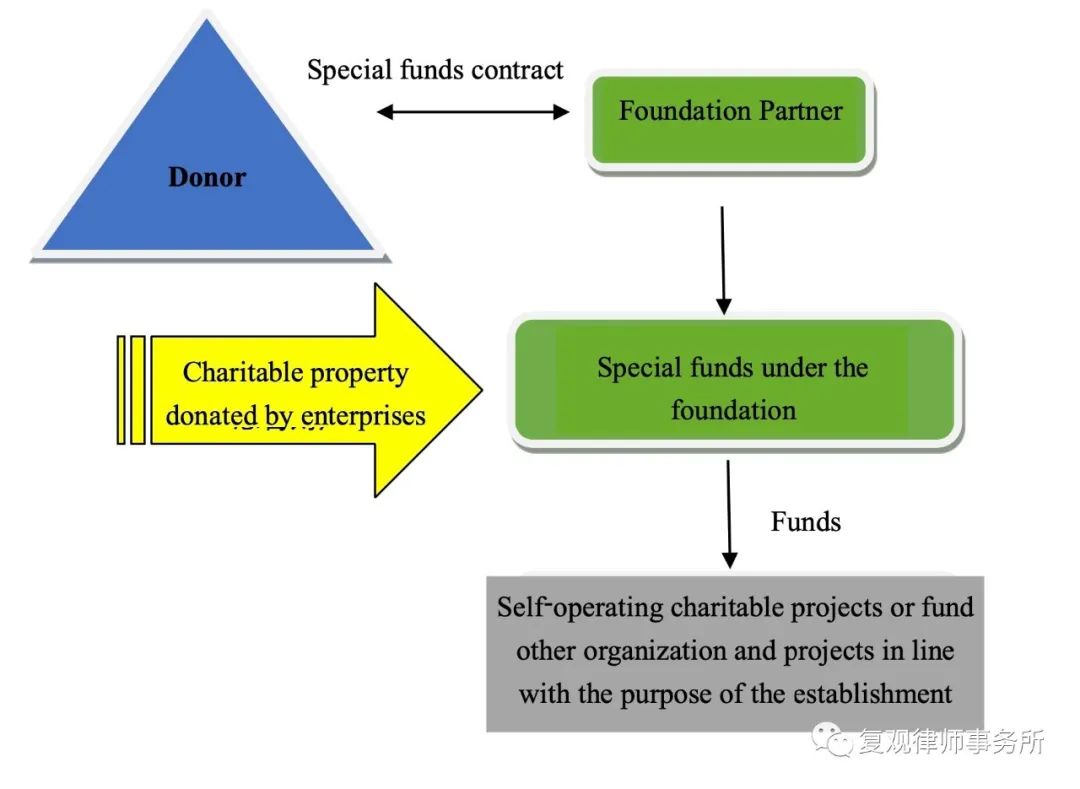
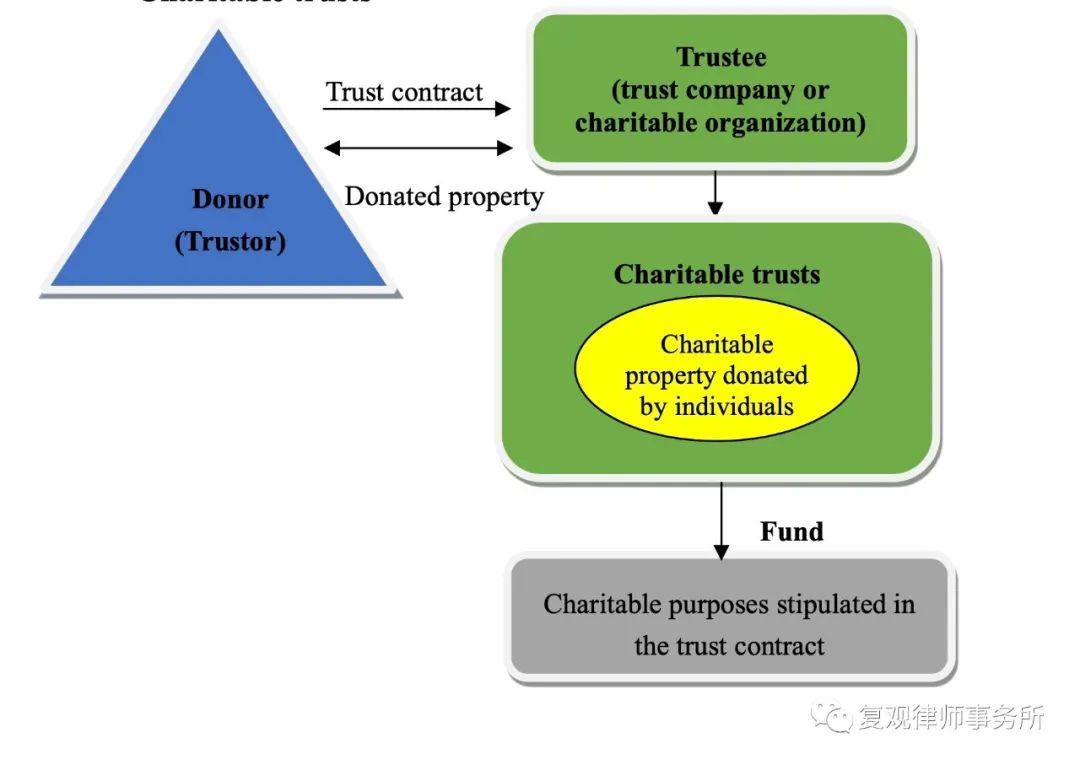
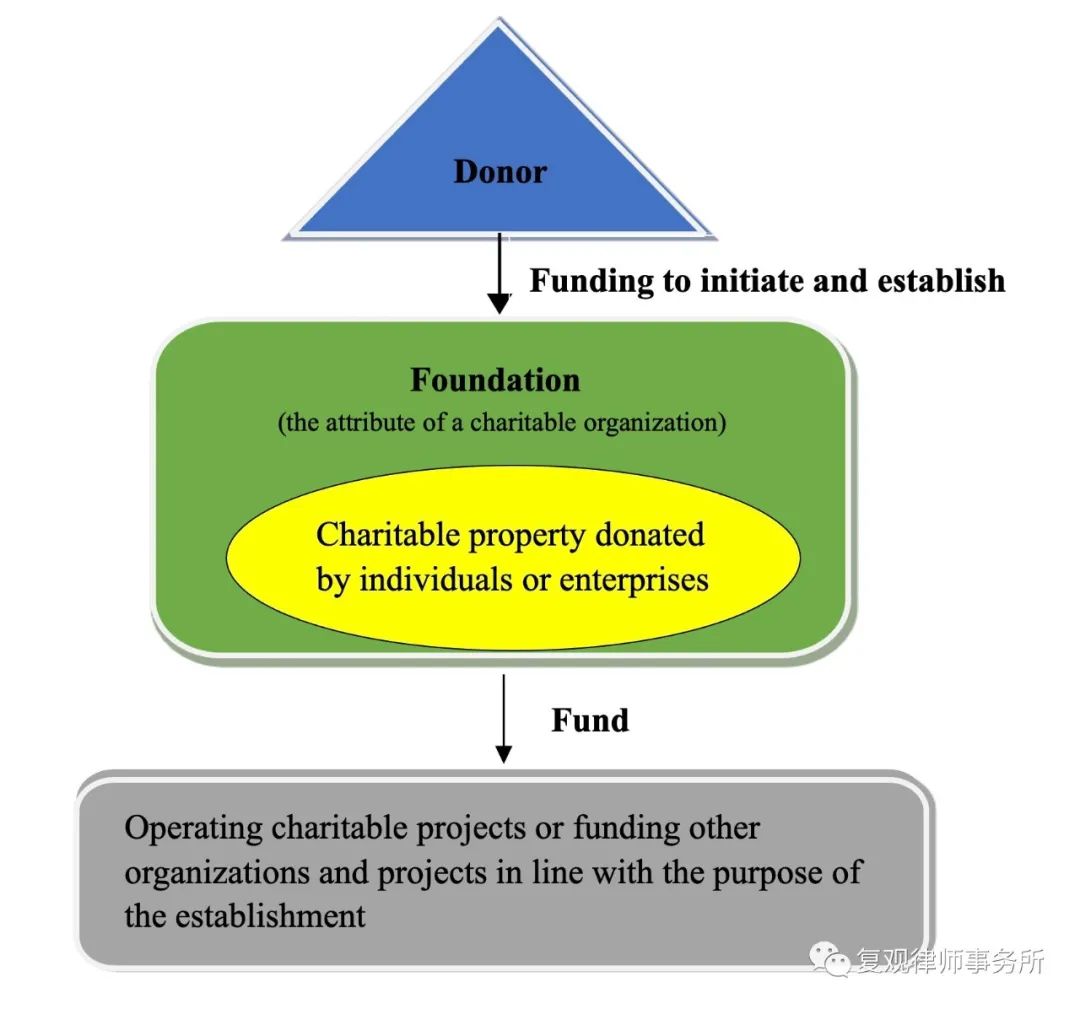
Under PRC Charity Law, cause-related marketing is not a legal term clearly defined; instead, it refers to the circumstances stipulated in Article 37 of PRC Charity Law, that is, “Natural persons, legal persons and other organizations that organize income-generating activities, such as performances, competitions, sales, auctions or other commercial activities, and that promise to use all or part of the proceeds for the purpose of charity”. Chinese law further requires that, “the purpose of charity” shall be realized by donating to “charitable organizations or other beneficiaries”, therefore, the sponsors of cause-related marketing like enterprises shall “sign a donation agreement with charitable organizations and other beneficiaries” before the business event and “fulfill their obligations after the event in accordance with the donation agreement, and make public the status of the donation”.
It should be noted that “charitable donations” under Chinese law, as long as they are designed for charity, include both donations to charitable organizations and direct donations to beneficiaries, and one of the significant differences between the two is that only donations to charitable organizations are eligible for tax benefits. Regarding the practical needs of corporate donation, this thesis will only discuss the cause-related marketing of corporate donation to charitable organizations.
Legal Relation in Cause-related Marketing
As can be seen from the previous description of cause-related marketing under China’s Charity Law, typical cause-related marketing includes enterprises, charitable organizations, and the public (consumers), and the legal relationship between them is as follows:
1 The relationship between enterprises and the public (consumers)
As cause-related marketing is in essence still a business behavior carried out by enterprises, therefore, the legal relationship between enterprises and the public (consumers), such as sales contract relationship and service contract relationship, is based on the nature of marketing, which does not fall under the regulatory scope of the Charity Law, but is subject to the Civil Code that regulates contractual relations, the Consumer Law that protects the rights and interests of consumers, the legal norms that regulate product quality, and the Advertising Law if it involves advertising. Advertisers shall be responsible for the authenticity of advertising content and shall not deceive or mislead consumers with false or misleading advertisements. For example, a typical violation of the Advertising Law is when the actual performance of a donation does not match the advertised performance.
2 The relationship between enterprises and charitable organizations
In cause-related marketing, the relationship between enterprises and charitable organizations is complicated. Such a relationship includes not only the contractual donation relationship regulated by charity law but also the authorization and licensing relationship of relevant intellectual property rights established by enterprises and charitable organizations due to their cooperation in cause-related marketing. Other relationships include contractual relationships that require cooperation between the two parties in cause-related marketing.
As donors of charitable donations, enterprises enjoy rights and obligations. The rights of a donor include determining, inquiring about, and supervising the use of donated properties by charitable organizations. The obligations of a donor include 1) delivering donated properties in accordance with the agreement with the charitable organizations; 2) not attaching unreasonable requirements for the charitable organizations to publicize their products or services, and 3) not appointing an interested person as the beneficiary of the charitable donation. As a sponsor of marketing activities, an enterprise needs to use the name, logo, and trademark of a charitable organization or the name and trademark of a charity project in its cause-related marketing. The charitable organization also needs to cooperate with other matters in the cause-related marketing. Therefore, an enterprise needs to enter into an agreement with a charitable organization on issues beyond the donation.
The Process for Enterprises to Carry Out Cause-related Marketing
Step1 Selecting a charitable organization
In order to achieve good results in marketing activities, enterprises should select charitable enterprises and cooperative charitable organizations that are related to the characteristics of the goods or services they operate, the brand images of the enterprises, and the values of the enterprises. Under Chinese law, a charitable organization is an identity attribute recognized by law, including the three types of NGOs, being the foundation, social service organization, and social group. Therefore, not all NGOs have the attributes of a charity organization. Enterprises should verify whether the NGO they intend to cooperate with has the attributes of a charitable organization by requiring it to provide the registration certificate with the identity of a charity organization or inquiring through the official channels of the Chinese government(https://cszg.mca.gov.cn/).
Step 2 Entering into an appropriate agreement with the charitable organization
Prior to cause-related marketing, it is required by Chinese law to enter into donation agreements with charitable organizations, which means that enterprises should fulfill their obligation to enter into donation agreements with charitable organizations in advance before they can use the names and other charitable resources of charitable organizations to carry out case marketing. In addition to matters involved in donation, matters that need cooperation between enterprises and charitable organizations must also be determined through agreements. Therefore, a “cooperation agreement” between an enterprise and a charitable organization specifying the content of donations is a more appropriate approach. Such an agreement should include:
• The duration of the cause-related marketing;
• The specific proportion or calculation method of corporate donation in operating income;
• Delivery time and method of donated property;
• Specific use of donated property;
• Issuance of donation notes;
• Authorization of the use of the names, trademarks, logos, etc. of the charitable organizations or charity projects;
• Specific matters requiring cooperation from charitable organizations: providing information on charity projects, assisting in information disclosure, etc.
Step 3 Performance of cause-related marketing and donation
Enterprises need to promote their goods or services and make donations under agreements with charitable organizations. Special care should be taken to align the content of marketing campaigns with agreements entered into with charitable organizations.
Step 4 Information disclosure
Under Chinese law, it is required for enterprises to disclose their donations after a cause-related marketing campaign. At present, there is no officially designated platform for enterprises to disclose information about donations. We suggest that enterprises disclose their donations through the same media, official websites, and we-media platforms with the marketing campaign.
Compliance Risk Matters in Cause-related Marketing
Content of market campaign
There is no clear regulation in Chinese law on the specific contents that enterprises need to publicize in cause-related marketing. It is recommended that at least the following shall be indicated in the contents:
The enterprise is the donor;
The specific proportion of corporate donation in operating income;
The specific charitable organization receiving the donation;
Introduction of the basic information of the specific charity project supported.
The obligations and precautions of an enterprise as an advertiser
Enterprises shall comply with the legal requirements for advertisements and advertisers under Chinese law when promoting their products or services through cause-related marketing. It should be noted that such promotion of enterprises is still commercial advertising, other than public service advertising, due to the existence of charitable factors. Under Chinese law, public service advertising only refers to non-profit advertising.
As advertisers, enterprises shall be responsible for the authenticity of the advertisements involved in cause-related marketing, avoiding advertisements containing false or misleading content without deceiving or misleading consumers. Enterprises with their cause-related marketing violating the foregoing provisions may not only bear civil liability to the consumers whose rights and interests are infringed but also face a fine from the market supervision administration.
Cause-related marketing by multinational companies worldwide
Multinational companies tend to lay out their CSR practices globally. When any element of the corporate marketing or charitable organization involved is not in China, the application of cause-related marketing under Chinese law can be classified as follows:
Cause-related marketing that carries out business activities in China and makes donations within China is the one under Chinese law;
Cause-related marketing that carries out business activities in China and makes donations outside China is not the one under Chinese law. This is because charitable organizations in cause-related marketing only refer to foundations, social service organizations, and social groups registered in China, excluding organizations of any nature outside China. However, if the beneficiary is an overseas NGO, it may constitute that the overseas NGO carries out activities in China. The legal analysis of cause-related marketing here is based on the fact that the State does not extend the definition of “other beneficiaries” in Article 37 of the Charity Law.
Sales outside China and donations within China are generally not subject to the compulsory jurisdiction of Chinese law unless a relevant contract between the enterprise and the domestic charity organization stipulates that Chinese law shall apply. This is an overseas donation, which is a donation directly from a foreign enterprise and is subject to the provisions on overseas donation under Chinese law.
Evaluating whether it constitutes a public fundraising
Public fundraising by charitable organizations is strictly controlled under Chinese law and requires compliance with a series of legal norms, among which the main legal requirements include: Charitable organizations need to qualify for public fundraising, file public fundraising records in advance, and disclose detailed information about public fundraising. An organization that is not qualified for public fundraising shall be subject to administrative punishment by relevant administrative departments if it raises funds publicly without authorization. Suppose an enterprise chooses to conduct a cause-related marketing campaign that is not a public fundraising activity. In that case, it should avoid constituting a public fundraising activity and take the following actions during cause-related marketing:
Receiving payments from the public (consumers) only by selling goods or services to them;
Avoiding claiming that payments paid by the public (consumers) will be donated directly to charitable organizations;
Avoiding misleading the consumers that they are donating instead of buying;
Only publicizing the enterprise itself as a donor and avoiding claiming that the public
(consumers) are donors.
Consequences and defense basis of enterprises not fulfilling donation obligations
The public announcement of donation and the conclusion of donation agreement by enterprises in cause-related marketing are all donation commitments. Charities can apply for a payment order or file a lawsuit requiring the enterprise to make the donation if it violates its donation commitments. However, there is an exception that an enterprise can use as a basis for defense: When “the economic situation of the enterprise has significantly deteriorated, seriously affecting its production and operation”, the enterprise can cease to perform its donation obligation, conditioned that it first report to relevant civil affairs administration responsible for charity in the place where the agreement is concluded and explain the situation to the society.
Tax Preferences
Charitable donations made by enterprises through cause-related marketing can enjoy a tax preference if they comply with the provisions of Chinese laws.
Such a tax preference is reflected in the preferential treatment for corporate income tax, that is, donations made by enterprises to charitable organizations within 12% of their total annual profits are allowed to be excluded from the calculation of taxable income. Conditions for enterprises to enjoy such as tax preference include:
1 Charitable organizations receiving donations are eligible for pre-tax deductions for public welfare donations
The central or local departments of finance, taxation, and civil affairs will regularly issue the Announcement on the List of Pre-tax Deduction Qualifications for Public Welfare Social Organizations, which can be used to verify the qualification of the charitable organization. In addition, as the charitable organization’s pre-tax deduction qualification for public welfare donation is valid for three years, it is necessary to also verify whether the pre-tax deduction qualification for public welfare donation of the charitable organization is valid.
2 Obtaining of the public welfare donation notes issues by the charitable organizations
An enterprise that donates to a charitable organization shall require the charitable organization to issue a public welfare donation note corresponding to the donation amount. The public welfare donation notes affixed with the seal of the financial department at or above the provincial (inclusive) level and the official seal of the donor are the legal public welfare donation notes. Operational receipts issued by charitable organizations cannot be used as evidence of pre-tax deduction of donations, and the donation expenditure incurred cannot be with a pre-tax deduction from corporate income tax.
3 The carry-over period does not exceed three years
Enterprises shall promptly declare the donation to the tax department for the pre-tax deduction. In normal circumstances, such a declaration shall be made in the year of the donation. If a tax deduction is not made in the year the donation is made, it is allowed to be carried forward to a later year, but the carry-forward time shall not exceed three years from the year following the donation is made.
Summary and Suggestions
China’s legal regulations on cause-related marketing aim to protect the legitimate rights and interests of charitable organizations and the public participating in charity and regulate charitable activities. Meanwhile, enterprises gain profits and improve the corporate image from cause-related marketing. Any violation of the law by enterprises in cause-related marketing may cause greater damage to the reputation of enterprises or charitable organizations than other marketing. Therefore, enterprises should ensure that they facilitate planning and compliance audits before launching cause-related marketing to meet the requirements of the law.